
Modern industry relies on various bearing types to keep machinery running smoothly. From mining and manufacturing to transportation and agriculture, bearings ensure the reliable performance of heavy-duty equipment. Bearings are critical in facilitating movement and handling mechanical loads across multiple sectors.
In this article, we will explore six common bearing types and their specific applications, from traditional ball bearings to advanced roller designs, demonstrating how they contribute to the efficient operation of industries worldwide.
What are bearings, and how do they work?
Bearings are critical components in a wide range of industrial equipment. Thousands of essential items could not function without them. Bearings are tribological components, defined as interacting surfaces involved in relative motion. Other examples include seals, piston rings, and electrical brushes.
Design elements
Bearings come in many shapes and sizes and are designed to support a specific type of motion. Depending on the wider system and its loading and movement demands, they are confined to limited degrees of freedom. Bearings are used for different applications and have several standard design features.
- They have three parts, with a rolling element between the inner and outer rings.
- The ring arrangement is called a “raceway”, and rolling elements include either balls or rollers.
- Along with these central components, bearings also include a cage, which retains the rolling element to prevent unwanted impacts and movement.
The elements are designed with a very specific purpose: to reduce friction and support loads. They prevent direct metal-to-metal contact between elements in relative motion, reducing wear and tear and energy consumption.
They also affect weight distribution, moving the load to the housing instead of the rotating element.
Types of uses: Where bearings are found
Bearings are found in a wide range of products. There are thousands in railway stock, aircraft engines, and wind turbines. Bearings are extremely common in industrial machinery, from motors and gearboxes to pumps and conveyors. They are central in numerous machinery classes and are used daily across multiple industry sectors.
Manufacturing, oil and gas, construction, and marine industries rely on heavy-duty machinery. Depending on the application, various bearing designs are suitable for these sectors. For example:
- Thrust ball bearings provide rigidity to sustain higher axial loads.
- Tapered roller bearings are also standard, especially for commercial vehicle applications.
- Hydro-static bearings are another example, and this design can support heavy loads by limiting relative motion.
Applications of bearing types in various industries
Depending on the type of structure and surrounding machinery, bearings offer many benefits. Industries use proven designs to support specific use cases and operating environments.

When the right bearings are selected for the task at hand, operators can expect the following benefits:
- Enhanced operational efficiency
- Increased equipment lifespan
- Reduced maintenance costs
Along with these general benefits, there are also industry-specific advantages:
- Mining: Bearings support high loads and extreme operating conditions.
- Manufacturing: Bearings enable design precision and promote durability.
- Oil and gas: Bearings can be used in high-pressure environments.
- Construction: Bearings enable heavy-duty performance in all conditions.
- Agriculture: Bearings are durable in harsh environments and weather.
- Wind energy: Bearings can be used in extreme operating conditions.
The six bearing types you need to know
Different bearing types are designed to support different applications. While the basic configuration of each bearing is the same, the rolling element and ring structure can be designed in various ways. The following bearing types are common:
Ball bearings
The most familiar is the ball bearing type, with a row of balls used as the rolling element. The balls are trapped between metal pieces known as races, with the outer race stationary and the inner race free to rotate. Ball bearings provide very low friction, so they are ideal for centrifugal pumps and railroad axles, among other applications.
There are many types of ball bearings, including deep groove ball bearings, thrust ball bearings, self-aligning ball bearings, and angular contact ball bearings.
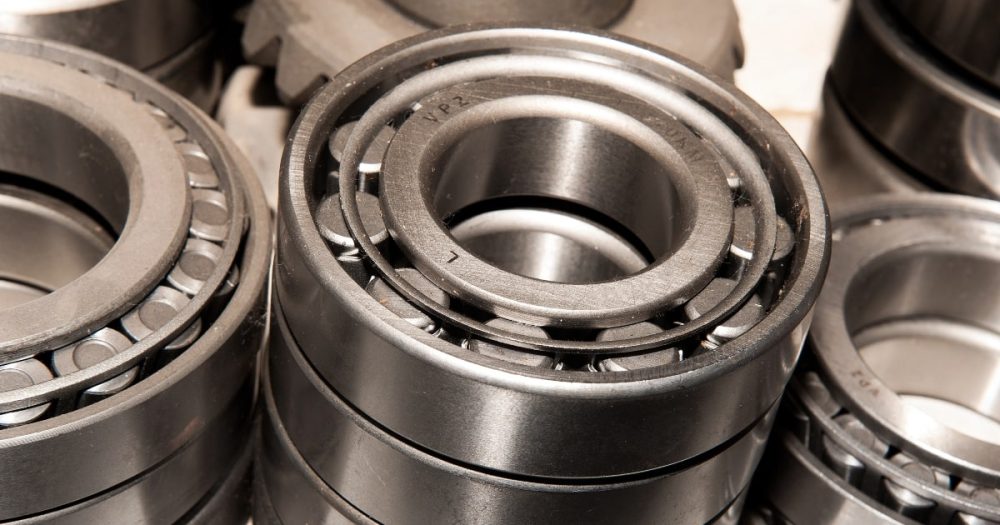

Roller bearings
Roller bearings are also known as rolling element bearings. These bearings swap balls for wider elements, where the length of the component is longer than its diameter. Rollers are designed to contact the inner and outer raceways, making them better equipped for heavy-duty applications. For example, these designs are used for agricultural machinery, food manufacturing equipment, and mining vehicles.
Roller bearings include spherical roller bearings, tapered roller bearings, needle roller bearings and cylindrical roller bearings.
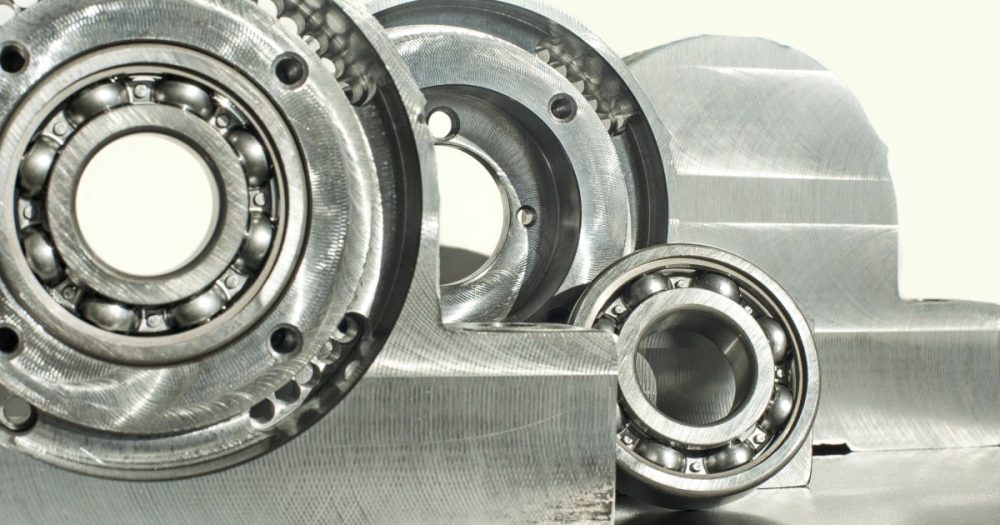
Plain bearings
Plain or sliding contact bearings feature a simple design with a plain surface and no dedicated rolling element.
They have a high load-carrying capacity and can accommodate misalignment and multidirectional movements. Plain bearings are used extensively in the agriculture, marine, automotive, and construction sectors.
The most common plain bearing is a bushing. Other examples of plain bearings include two-piece bearings and integral bearings.
Fluid bearings
Fluid bearings are an alternative to metallic bearings for specific applications. They help increase critical components’ lifespan while reducing noise and vibration levels. They have a higher initial cost than other bearings but also help reduce vibration, maintenance and replacement expenses.
Fluid bearings use pressurised gas or liquid to carry loads with minimal friction, making them ideal for hydroelectric plants, turbines and generators, and marine propeller shafts. Fluid bearings are classified as either hydrostatic bearings or hydrodynamic bearings.
Magnetic bearings
Magnetic bearings use magnetic levitation and don’t rely on physical contact. This gives them fantastic wear properties and makes them ideal for high-speed applications. Magnetic bearings are used for electrical power generation, machine tools, and natural gas handling, among other applications.
Types of bearings include active magnetic bearings and passive magnetic bearings. The former uses electromagnets around the shaft, while the latter uses permanent magnets to create a magnetic field.
Linear motion bearings
This category is different from the others. Instead of describing the type of bearing based on specific configurations and components, it refers to a purposeful design limitation. For this reason, all of the bearings listed above can be made into linear motion bearings.
Also known as a linear slide, this bearing type is designed to provide only free motion in one direction. Examples include machine slides, X-Y tables, and roller tables.
Is it time to replace your bearings?
At Statewide Bearings, we specialise in quality bearings for industrial applications.
We have many ball bearings, roller bearings, housings and sealing solutions for machinery and heavy loads across industries. Explore our range of bearings and power transmission products to enhance your business operations.
If you have any further questions, please contact us today!



